The “kissing bug” may sound like an innocuous name, but this blood-sucking insect is actually a vector for a dangerous and potentially life-threatening disease. Chagas disease, also known as the “kissing bug disease,” is a growing public health concern, especially in parts of the Americas where these bugs are prevalent.
As climate change and human encroachment on natural habitats continue to drive the spread of kissing bugs, it’s more important than ever to understand the risks and how to protect yourself.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll dive deep into the world of the kissing bug, exploring the disease it carries, the symptoms to watch for, and the steps you can take to stay safe.
What is the Kissing Bug Disease?
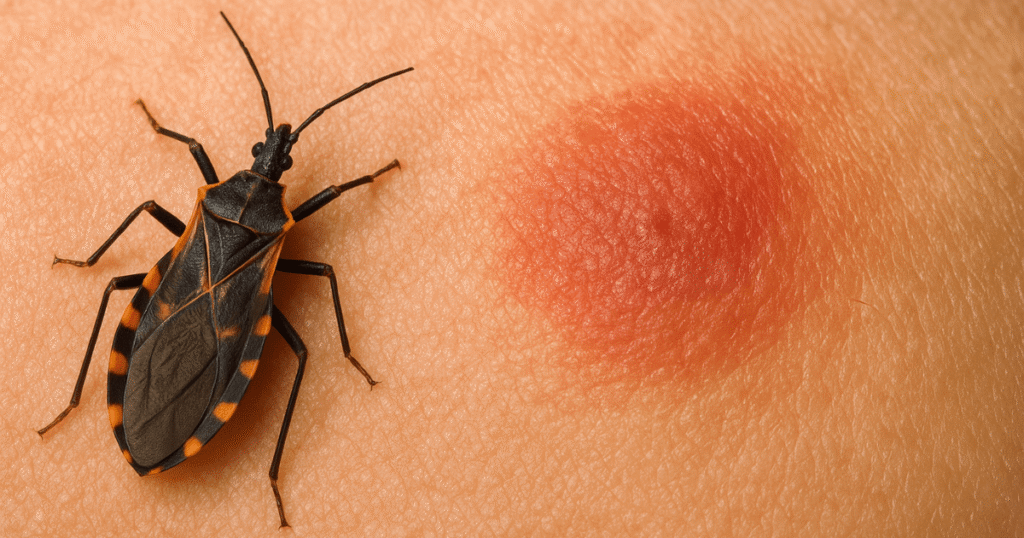

Kissing bug disease, or Chagas disease, is a parasitic infection caused by the Trypanosoma cruzi parasite. This parasite is transmitted primarily by blood-sucking insects called triatomine bugs, which are more commonly known as “kissing bugs.”
These insects get their name from their tendency to feed on the faces of sleeping humans, often near the lips or eyes. When an infected kissing bug defecates near the bite wound, the parasite can enter the body through the skin or mucous membranes, leading to the infection.
How is Kissing Bug Disease Transmitted?
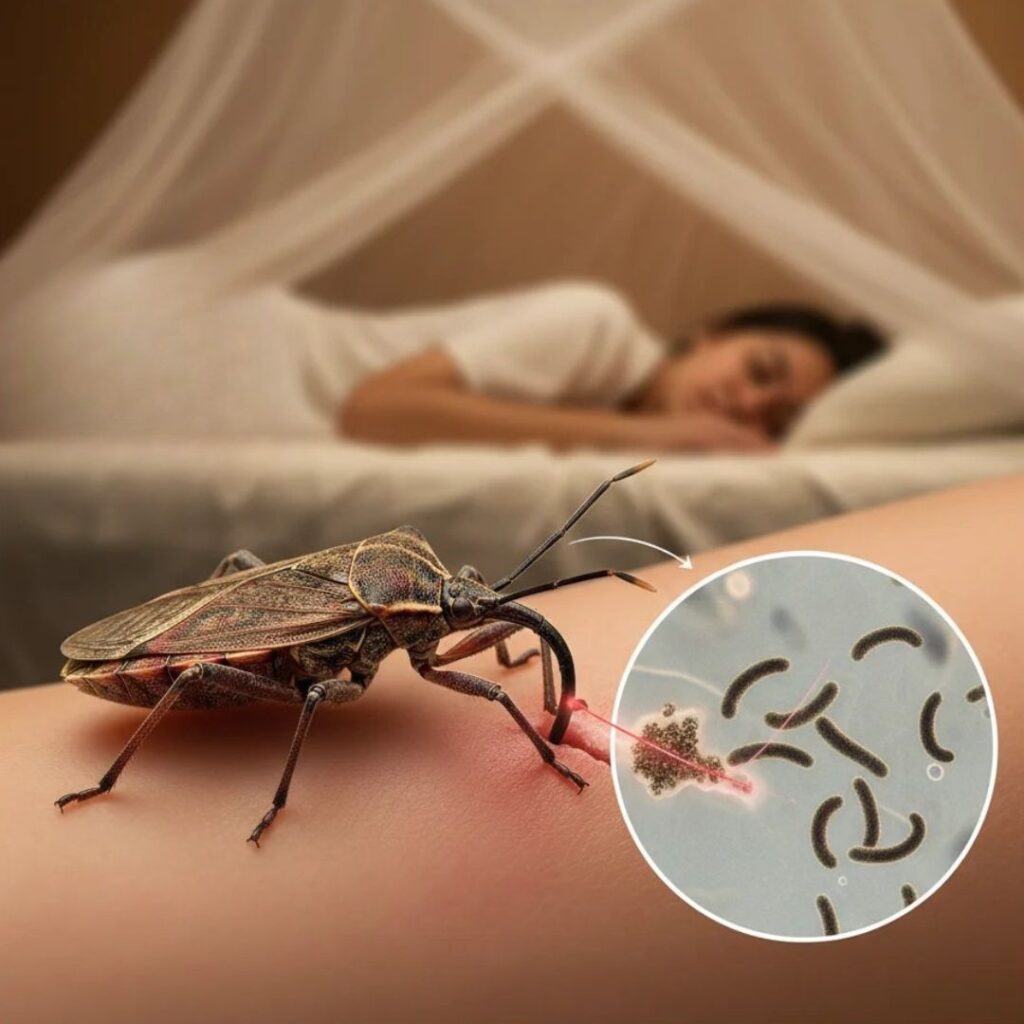

Kissing bugs become infected with the T. cruzi parasite by feeding on the blood of infected animals or humans. The parasite lives in the bug’s digestive system and is passed through its feces. When a kissing bug bites a person, it may defecate near the bite, allowing the parasite to enter the body.
In addition to the direct transmission from bug to human, Chagas disease can also be spread through:
- Blood transfusions or organ transplants from infected donors
- Congenital transmission from an infected mother to her child during pregnancy
- Ingestion of food or drink contaminated with the parasite
Symptoms of Chagas Disease
Chagas disease has two main stages: the acute stage and the chronic stage.
Acute Stage:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Body aches
- Rash
- Diarrhea
- Vomiting
- Swelling around the bite site (known as a “chagoma”)
Chronic Stage:
- Many people may not experience any symptoms for years or decades after the initial infection.
- However, the parasite can cause severe damage to the heart, digestive system, and nervous system over time.
- Complications can include heart rhythm abnormalities, enlargement of the esophagus or colon, and even sudden cardiac death.
Diagnosing and Treating Chagas Disease
Chagas disease can be difficult to diagnose, as the early symptoms are often nonspecific and easily mistaken for other illnesses. Diagnostic tests, such as blood tests or biopsies, are typically needed to confirm the infection.
Treatment:
- Antiparasitic medications, such as benznidazole or nifurtimox, are the primary treatment for Chagas disease.
- These drugs are most effective in the acute stage, but they can also be used to treat chronic cases, though the success rate is lower.
- Treatment can have significant side effects, so it’s important to work closely with a healthcare provider.
Prevention:
- Avoiding contact with kissing bugs is the best way to prevent Chagas disease.
- Improving housing conditions, particularly in rural areas, can help reduce the risk of kissing bug infestations.
- Blood and organ donor screening is also crucial to prevent the spread of Chagas disease through medical procedures.
The Growing Threat of Kissing Bug Disease

Chagas disease is endemic to Latin America, where it has been a public health concern for decades. However, in recent years, the disease has been increasingly reported in other parts of the world, including the southern United States.
Several factors are contributing to the spread of kissing bug disease:
- Climate change: Warming temperatures and changing weather patterns are allowing kissing bugs to expand their range into new areas.
- Human encroachment: As people move into rural areas and disturb natural habitats, they come into closer contact with kissing bugs.
- Increased awareness and testing: More people are being tested and diagnosed with Chagas disease, leading to a better understanding of its prevalence.
Protecting Yourself from Kissing Bug Disease
While the thought of a “kissing bug” may be unsettling, there are steps you can take to reduce your risk of contracting Chagas disease:
- Avoid contact with kissing bugs: If you live in or travel to areas where kissing bugs are common, be vigilant about checking for these insects in and around your home.
- Improve housing conditions: Ensure that your home is well-sealed, with no cracks or crevices where kissing bugs can enter.
- Use insecticides: Regularly applying insecticides around the exterior of your home can help deter kissing bugs.
- Seek medical attention for suspicious symptoms: If you develop any symptoms of Chagas disease, especially after traveling to an endemic area, don’t hesitate to see a healthcare provider.
- Support research and awareness efforts: Donate or volunteer with organizations working to combat the spread of Chagas disease and improve treatment options.
Conclusion: Stay Informed, Stay Safe
The kissing bug disease may not be a household name like other infectious diseases, but it’s a growing threat that requires our attention and action.
By understanding the risks, recognizing the symptoms, and taking proactive steps to protect ourselves, we can help prevent the further spread of this dangerous parasitic infection.
Remember, knowledge is power when it comes to safeguarding your health. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and don’t hesitate to seek medical care if you have concerns.
Together, we can work to keep the “kissing bug” at bay and protect ourselves from the dangers of Chagas disease.
FAQs
What is the “kissing bug”?
The “kissing bug” is a blood-sucking insect that can transmit the parasite that causes Chagas disease, also known as the “kissing bug disease.”
How do you get Chagas disease?
Chagas disease is primarily transmitted through the feces of infected kissing bugs. When an infected bug bites a person and defecates near the bite, the parasite can enter the body through the skin or mucous membranes.
What are the symptoms of Chagas disease?
Chagas disease has two main stages: the acute stage, which can cause fever, fatigue, and swelling, and the chronic stage, which can lead to severe heart and digestive system complications years later.
Is there a cure for Chagas disease?
Yes, antiparasitic medications can effectively treat Chagas disease, especially in the early, acute stage. However, chronic cases are more difficult to treat, and supportive care is crucial for managing the long-term effects.
How can I prevent Chagas disease?
Avoiding contact with kissing bugs, improving housing conditions, and supporting research and awareness efforts are all important steps to prevent the spread of Chagas disease.
